|
Medical Confidentiality
Information about a person's ability to work is not a confidential matter. A person's work capacity issue is discussed through:
| a. | Certificates of capacity |
| b. | Return to work plans |
| c. | Conversations between the employee and supervisor |
| d. | Discussions between providers |
However, while not confidential the information is personal and should be dealt with in a way that is respectful of the person. Information should be provided to others on a need to know basis.
Many other issues in relation to work injuries are confidential. The person's permission or consent should be obtained prior to asking a treating practitioner to provide confidential information.
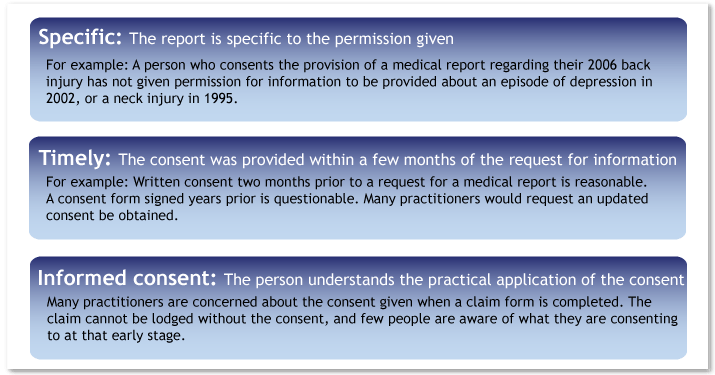
Consent to provide information can be a challenging area. Medical practitioners consider that consent should be specific to the condition, timely, and provided by a person who understands what they are consenting to.
Written versus verbal consent
Written consent is the most common form of consent. Patients provide written consent for procedures, surgery, providing medical reports. Written consent is the most appropriate form of consent for a medical report to be provided.
If a treating practitioner has a good relationship with the person, and a matter needs to be dealt with expeditiously, the treater may obtain verbal consent.
For example, a request for a report is received by the doctor, but the consent accompanying the report was signed years prior. The treater may call the patient and check they are aware of the request for the report, and that they wish the report to be provided.
Dealing with the issue of consent is not generally difficult. However the consent issue should be dealt with proactively. Consent issues don't generally cause problems when relationships are positive.
Privacy of records at the workplace
Medical information provided to the workplace needs to be kept private. A locked cabinet is appropriate storage for files that contain:
| • | Medical reports, including copies of treaters' notes |
| • | Medical invoices or billing information |
| • | Case file notes that record information provided by treaters, in writing or through telephone conversations |
| • | Copies of investigation results, such as XRs or scans |
![]() What's Next?
What's Next?
RTW Co-coordinator competencies